
What is the center wavelength of a laser?

Laser wavelength refers to the output wavelength of the laser, which is an important parameter of the laser output laser beam, and the corresponding output frequency is called the laser frequency.
What is a laser?
Ordinary light (lights, etc.) differs from lasers as follows.
The laser emits a beam with high directivity, that is, the composed light waves propagate in a straight line without spreading. Light waves from ordinary light sources spread out in all directions. The light waves in the laser beam are all the same color (this property is called monochromaticity). Ordinary light (such as the light emitted by fluorescent tubes) is generally a mixture of several colors of light that appear white. As the light waves within a laser beam propagate, they oscillate with perfectly synchronized peaks and troughs, a property called coherence. When two laser beams overlap each other, the peaks and troughs of each beam only reinforce each other, creating an interference pattern.
| Ordinary Light | Laser Beam | |
|---|---|---|
| Directivity (light waves travel in straight lines) |
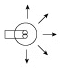 light bulb light bulb |
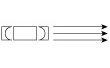 laser laser |
| Monochromaticity | 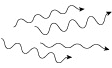 many different wavelengths many different wavelengths |
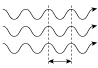 Single wave Single wave |
| Coherence |  Crest and trough alignment scattered Crest and trough alignment scattered |
 The peaks and valleys are aligned The peaks and valleys are aligned |
What is the laser wavelengthThe laser wavelength refers to the output wavelength of the laser, which is an important parameter of the laser output laser beam, and the corresponding output frequency is called the laser frequency. The wavelength unit of laser is usually measured in nm (1/1000000000 meter), and laser can be divided into two categories: visible laser and invisible laser.
What is visible light
The wavelength range of electromagnetic waves that the human eye can perceive is called "visible light". The short wavelength of visible light is about 360 to 400 nm, and the long wavelength is about 760 to 830 nm, and if the wavelength is outside the wavelength range of "visible light" (shorter or longer), it is beyond the range that the human eye can perceive.
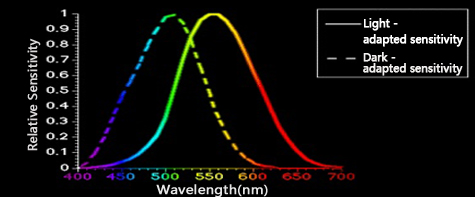
Under normal circumstances, the wavelength of visible light that the human eye can clearly distinguish is basically between 400 nanometers and 700 nanometers. The shorter the wavelength of the laser, the bluer and more violet its color is, down to ultraviolet rays invisible to the human eye. However, the longer the wavelength, the more reddish its color becomes, all the way to infrared, which is invisible to the human eye. The human eye is most sensitive to green, orange and yellow light with wavelengths between 550-570 nanometers. Therefore, in the visible light range, wavelength can be understood as a numerical identification of color.
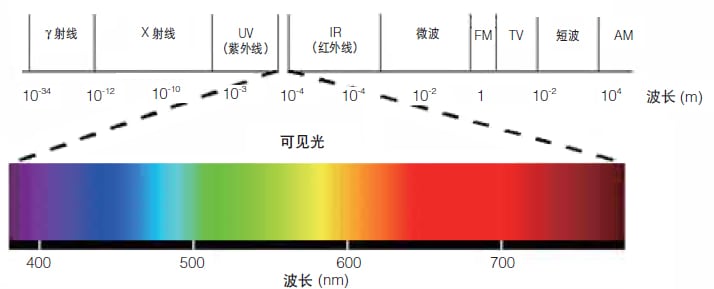
The wavelengths of the visible beams of the laser from short to long are:blue-violet (375nm, 405nm), blue (445nm, 488nm), green (520nm, 532nm), yellow (589nm) , 577nm) and red (635nm, 650nm); lasers in this wavelength range are usually used in stage performances and medical fields.
Types of lasers
It can be roughly divided into three types: solid, gas, and liquid
Applicable lasers vary depending on the intended processing application.
Solid
Nd:YAG
YAG (Yttrium, Aluminum, Garnet)
Basic wavelength (1064 Nm)
Mainly used for general engraving
Frequency double (532 Nm) (green laser)
For imprinting on materials such as silicon wafers
Used for fine printing and processing
Frequency triple (355 Nm) (UV laser)
Used for ultra-fine processing such as LCD printing, repair processing, VIA via processing, etc.
Liquid crystal repair processing…Removal of resin coating for repair process
VIA Via Processing…PCB Hole Processing
YAG Laser (Nd:YAG)
YAG lasers are commonly used in a variety of marking applications, such as marking plastic and metal workpieces, as well as machining applications. The invisible near-infrared beam emitted by the YAG laser has a wavelength of 1064 nm.
YAG is a solid yttrium aluminum garnet with a crystal structure. With the addition of a light-emitting element, here Nd (neodymium), the YAG crystal enters an excited state after absorbing the light from the laser diode.
Nd:YVO4(1064 nm)
YVO4(yttrium vanadate)
For very small text marking
High peak energy with high Q-switching frequency
Good energy conversion efficiency
YVO4Laser (Nd: YVO4)
YVO4The laser can be used for ultrafine marking and machining applications. The YVO4laser emits an invisible near-infrared beam with a wavelength of 1064 nm, the same as the YAG laser.
YVO4 is a Y (yttrium) V (vanadium) O4 (oxide), or YVO4 (yttrium vanadate) solid with a crystal structure . With the addition of a light-emitting element, here Nd (neodymium), the YAG crystal enters an excited state after absorbing the light from the laser diode.
Yb: Fiber (1090 nm)
Yb (Yttrium)
For high output marking
The large surface area of the booster media makes it easy to achieve high output
High cooling efficiency can simplify cooling equipment and achieve miniaturization
LD (650 to 905 nm)
Semiconductor Lasers (GaAs, GaAlAs, GaInAs)
Gas
CO2(10.6μm)
For processing equipment, marking, laser surgery
CO2Laser
CO2lasers are primarily used for machining and marking applications.
CO2The laser emits an invisible infrared beam with a wavelength of 10.6 μm. N2 nitrogen can be used to increase the energy level of CO2, and helium can be used to stabilize the energy level of CO2.
He-Ne laser (630 nm)
typically (red)
For measurers (shape measurement, etc.)
For common laser measuring instruments on the market (for shape measurement, etc. due to low output power)
Excimer Laser (193 nm)
For semiconductor light-leakage devices and ophthalmology
Laser can be generated in a relatively simple configuration by mixing inert gas and halogen gas
Deep ultraviolet (DUV) laser absorption is very high
(In ophthalmology, vision is corrected by evaporating the lens to focus on the retina)
Argon Laser (488 to 514 nm)
For physics and chemistry
Able to generate a variety of colors, mainly used in biological-related research institutes
Liquid
Dye (330 to 1300 nm)
For physics and chemistry
Fluorescence of excited pigments by laser
Characteristics of each wavelength
Wavelength: 10600 nm
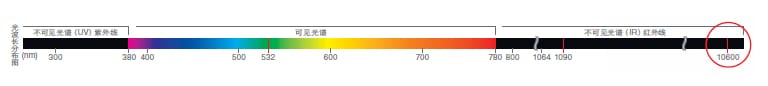
CO2The wavelength of the laser is ten times longer than that of a YAG, YVO4 or fiber laser. This is the longest wavelength among the widely used industrial lasers. As the name suggests, it is generated by excitation with CO2 gas as the laser medium.
Typical characteristics of lasers in the 10600nm wavelength region
![<?=$public_r['add_com']?>](https://en.pulse-x.com/d/file/p/2025/04-07/bf59db14fcdf89bedbf6a9fdeeae3c9e.png)
Send Message To Us!